DNA Replication
- Replication is the copying of DNA from parental DNA.
- Watson & Crick proposed the Semi-conservative model of replication. It suggests that the parental DNA strands act as a template for the synthesis of new complementary strands. After replication, each DNA molecule would have one parental and one new strand.
- Matthew Messelson & Franklin Stahl (1958) experimentally proved the Semi-conservative model.
Messelson & Stahl’s Experiment
- They grew E. coli in 15NH4Cl medium (15N = heavy isotope of nitrogen) as the only nitrogen source. As a result, 15N was incorporated into newly synthesised DNA (heavy DNA or 15N DNA).
- Heavy DNA can be distinguished from normal DNA (light DNA or 14N DNA) by centrifugation in a cesium chloride (CsCl) density gradient.
- E. coli cells from the 15N medium were transferred to a 14NH4Cl medium. After one generation (i.e., after 20 minutes), they isolated and centrifuged the DNA. Its density was intermediate (hybrid) between 15N DNA and 14N DNA. This shows that in newly formed DNA, one strand is old (15N type) and one strand is new (14N type). This confirms semi-conservative replication.
- After the second generation (i.e., after 40 minutes), there were equal amounts of hybrid DNA and light DNA.
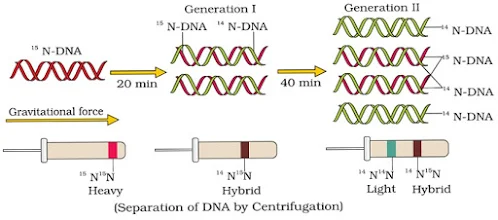
Messelson & Stahl’s Experiment
- Taylor & colleagues (1958) performed similar experiments on Vicia faba (faba beans) using radioactive thymidine to detect the distribution of newly synthesized DNA in the chromosomes. It proved that the DNA in chromosomes also replicates semi-conservatively.
The Machinery and Enzymes for Replication
- DNA replication starts at a point called origin (ori).
- A unit of replication with one origin is called a replicon.
- During replication, the 2 strands unwind and separate by breaking H-bonds in the presence of an enzyme, Helicase.
- Unwinding of the DNA molecule at a point forms a ‘Y’-shaped structure called a replication fork.

Watson-Crick model for semiconservative DNA replication

Replication Fork in DNA Replication
- The separated strands act as templates for the synthesis of new strands.
- DNA replicates in the 5’→3’ direction.
- Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates (dATP, dGTP, dCTP & dTTP) act as substrates and provide energy for polymerization.
- Firstly, a small RNA primer is synthesized in the presence of an enzyme, primase.
- In the presence of an enzyme, DNA-dependent DNA polymerase, many nucleotides join with one another to the primer strand and form a polynucleotide chain (new strand).
- During replication, one strand is formed as a continuous stretch in the 5’→3’ direction (Continuous synthesis). This strand is called the leading strand.
- The other strand is formed in small stretches (Okazaki fragments) in the 5’→3’ direction (Discontinuous synthesis).
- The Okazaki fragments are then joined together to form a new strand by an enzyme, DNA ligase. This new strand is called the lagging strand.
- If a wrong base is introduced in the new strand, DNA polymerase can do proofreading.
- E. coli completes replication within 18 minutes, i.e., 2000 bp per second.
- In eukaryotes, the replication of DNA takes place at the S-phase of the cell cycle. Failure in cell division after DNA replication results in polyploidy.
Select a Topic 👇
-
Topic 1: The DNA
Topic 2: The Search for Genetic Material
Topic 3: Properties of Genetic Material, RNA World
Topic 4: DNA Replication
Topic 5: Transcription
Topic 6: Genetic Code, Types of RNA
Topic 7: Translation (Protein Synthesis)
Topic 8: Regulation of Gene Expression, Operon Concept
Topic 9: Human Genome Project (HGP)
Topic 10: DNA Fingerprinting
