Inheritance of One Gene
Monohybrid Cross
- A cross involving 2 plants differing in one character pair. E.g., Mendel crossed tall and dwarf pea plants to study the inheritance of one gene.

Monohybrid Phenotypic and Genotypic Ratios
- Monohybrid phenotypic ratio: 3 Tall : 1 Dwarf = 3:1
- Monohybrid genotypic ratio:
- 1 Homozygous tall (TT)
- 2 Heterozygous tall (Tt)
- 1 Homozygous dwarf (tt)
- = 1:2:1
- Mendel made similar observations for other pairs of traits. He proposed that some factors were inherited from parent to offspring. Now it is called genes.
- Do not use T for tall and d for dwarf because it is difficult to remember whether T & d are alleles of the same gene or not.
- The F1 (Tt) when self-pollinated, produces gametes T and t in equal proportion. During fertilization, pollen grains of T have a 50% chance to pollinate eggs of T & t. Also, pollen grains of t have a 50% chance to pollinate eggs of T and t.
- 1/4th of the random fertilization leads to TT (¼ TT).
- 1/2 (2/4) of the random fertilization leads to Tt (½ Tt).
- 1/4th of the random fertilization leads to tt (¼ tt).
- Tt x Tt
- Binomial expression = (ax + by)2
- Hence (½ T + ½ t)2 = (½ T + ½ t)(½ T + ½ t) = ¼ TT + ¼ Tt + ¼ Tt + ¼ tt = ¼ TT + ½ Tt + ¼ tt
- Mendel self-pollinated the F2 plants.
- He found that dwarf F2 plants continued to generate dwarf plants in F3 & F4.
- He concluded that the genotype of the dwarfs was homozygous - tt.
Test Cross
- Crossing of an organism with a dominant phenotype to a recessive individual. E.g.,
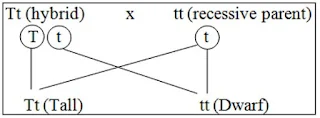
- Hence monohybrid test cross ratio = 1:1
- Test cross is used to find out the unknown genotype of a character. E.g.,

- Mendel conducted a test cross to determine the F2 genotype.
Mendel’s Principles or Laws of Inheritance
1. First Law (Law of Dominance):
- Characters are controlled by discrete units called factors.
- Factors occur in pairs.
- In a dissimilar pair of factors, one member of the pair dominates (dominant) the other (recessive).
2. Second Law (Law of Segregation):
- “During gamete formation, the factors (alleles) of a character pair present in parents segregate from each other such that a gamete receives only one of the 2 factors”.
- Homozygous parent produces similar gametes.
- Heterozygous parent produces two kinds of gametes.
Select a Topic 👇
-
Topic 1: Mendel's Experiments
Topic 2: Inheritance of One Gene
Topic 3: Inheritance of Two Genes
Topic 4: Other Patterns of Inheritance
Topic 5: Chromosomal Theory, Morgan's Experiment
Topic 6: Sex Determination
Topic 7: Mutation and Pedigree Analysis
Topic 8: Genetic Disorders (Mendelian and Chromosomal)
