HOW STRONG ARE ACID OR BASE SOLUTIONS?
- The amount of H⁺ ions present in a solution can be measured by using a universal indicator. It is a mixture of several indicators. It shows different colours at different concentrations of hydrogen ions.
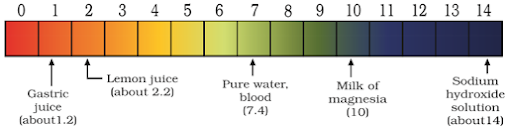
- A scale for measuring H⁺ ion concentration in a solution is called pH scale (p = ‘potenz’ in German = power).
- pH is measured from 0 (very acidic) to 14 (very alkaline).
- Higher the H⁺ ion concentration, lower is the pH value.
- pH of a neutral solution is 7.
- Values less than 7 represent an acidic solution.
- Values more than 7 represent an alkaline solution.
- pH value from 7 to 14 represents an increase in OH⁻ ion concentration, i.e., increase in the strength of alkali.
- Generally, paper impregnated with the universal indicator is used for measuring pH.

pH values of various solutions:
| Solution | Colour of pH paper | Approximate pH value | Nature of substance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Saliva (before meal) | Green | 6.8 – 7.4 | Slightly acidic to basic |
| Saliva (after meal) | Yellow green | 5.8 | Acidic |
| Lemon juice | Orange | 2.2 | Acidic |
| Colourless aerated drink | Yellow | 4.0 | Acidic |
| Carrot juice | Yellow green | 6.0 | Acidic |
| Coffee | Yellow | 4.5 | Acidic |
| Tomato juice | Yellow | 4.3 | Acidic |
| Tap water | Green | 6 – 8.5 | Varied |
| 1M NaOH | Dark blue | 14 | Basic |
| 1M HCl | Red | 0 | Acidic |
- The strength of acids and bases depends on the number of H⁺ ions and OH⁻ ions produced, respectively. For example, 1 molar hydrochloric acid and 1 molar acetic acid (same concentration) produce different amounts of H⁺ ions.
- Strong acids: Produce more H⁺ ions. E.g., HCl, H₂SO₄.
- Weak acids: Produce less H⁺ ions. E.g., CH₃COOH.
- Strong bases: Produce more OH⁻ ions. E.g., NaOH, KOH.
- Weak bases: Produce less OH⁻ ions. E.g., NH₄OH, Ca(OH)₂.
Importance of pH in Everyday Life
Plants and animals are pH sensitive. They can survive only in a narrow range of pH change.
Our body works at the pH range of 7.0 to 7.8.
When pH of rainwater is less than 5.6, it is called acid rain. When it flows into rivers, it lowers the pH of river water, adversely affecting the survival of aquatic life.
What is the pH of the soil in your backyard?
To find out the pH for healthy growth of a plant, collect the soil from various places and check their pH as given below:
- Put about 2 g soil in a test tube and add 5 mL water.
- Shake the contents of the test tube.
- Filter the contents and collect the filtrate in a test tube.
- Check the pH of filtrate using universal indicator paper.
Ideal soil pH for the growth of plants = 6 to 7.
pH in our digestive system
- The stomach produces hydrochloric acid.
- During indigestion, the stomach produces too much acid and causes pain and irritation.
- To get rid of pain, bases called antacids are used. They neutralize the excess acid. E.g., Magnesium hydroxide (Milk of magnesia), a mild base.
pH change as the cause of tooth decay
- Tooth enamel is made up of calcium hydroxyapatite (a crystalline form of calcium phosphate). It is the hardest substance in the body and does not dissolve in water.
- Bacteria in the mouth produce acids by degradation of sugar and food particles. Thus, enamel is corroded at a pH below 5.5, causing tooth decay.
- Using toothpaste (basic) can neutralize the excess acid and prevent tooth decay.
Self-defence by organisms through chemical warfare
- Bee stings leave formic acid, which causes pain and irritation. Applying a mild base like baking soda on the stung area gives relief.
- Stinging hair of nettle leaves injects methanoic acid, causing burning pain. A traditional remedy is rubbing the area with the leaf of the dock plant.
| Natural source | Acid | Natural source | Acid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinegar | Acetic acid | Sour milk (Curd) | Lactic acid |
| Orange | Citric acid | Lemon | Citric acid |
| Tamarind | Tartaric acid | Ant sting | Methanoic acid |
| Tomato | Oxalic acid | Nettle sting | Methanoic acid |
Acids in other planets: The atmosphere of Venus is made up of thick white and yellowish clouds of sulphuric acid.
