2020 SAY (+2)
PART A: ZOOLOGY
Answer any 3 questions from 1 - 5. Each carries 1 score. (3 x 1 = 3)
1.
Which among the following is an
example for homology?
(a)
The eye of the Octopus and of
Mammals
(b)
Sweet potato and potato
(c)
Thorns and tendrils of Bougainvillea
and Cucurbita
(d)
Wings of butterfly and of birds
2.
The embryo with 8 to 16 blastomeres
is called a ....................
(a)
Gastrula
(b)
Morula
(c)
Blastula
(d)
Trophoblast
3.
Select a female heterogametic animal
from the following:
(a)
Human beings
(b)
Drosophila
(c)
Birds
(d)
Grasshopper
4.
A free living nitrogen fixing
bacteria in the soil.
(a)
Rhizobium
(b)
Azospirillum
(c)
Nostoc
(d)
Anabaena
5.
Find out the initiator codon among
the following:
(a)
ACG
(b)
AUC
(c)
AUG
(d)
AAG
Answer any 9 questions from 6 – 16.
Each carries 2 scores. (9 2 = 18)
6. Observe the list of certain common
diseases in human given below and answer the following:
Common
cold, Malaria, Amoebiasis, Typhoid, Filariasis
(a)
Identify the bacterial disease among
the enlisted.
(b)
Name its causative organism.
(c)
Mention any two symptoms of it.
8. (a) Define Hardy – Weinberg
principle.
(b) List out any two factors affecting Hardy – Weinberg
Equilibrium.
9. Complete the table using appropriate
terms:
|
Klinefelter’s
syndrome |
(a) |
Sterile male |
|
(b) |
44A + XO |
(c) |
|
(d) |
Trisomy 21 |
Mental retardation |
10. Match the following:
|
|
11. Rearrange the following human
reproductive events in the correct order of their occurrence:
Lactation → Formation of Zygote → Insemination
→ Implantation → Fertilisation → Gametogenesis → Gestation → Parturition
12. In a cross between a true breeding red
flowered and a true breeding white flowered plants, the F1 generation was pink
coloured flowers. From this cross
(a)
Identify the Inheritance.
(b)
Give an example for this type of
Inheritance.
(c)
Write the F2 phenotypic and
genotypic ratio.
13. Diagrammatic representation of the
operation of natural selection on different traits is shown below:
I.
Identify ‘a’, ‘b’ and ‘c’.
II.
What is the evolutionary
significance of ‘b’?
14. (a) Complete the flow chart given
below showing DNA finger-printing technique.
(b) Who developed the DNA finger-printing technique?
(c) Write the full form of VNTR.
15. Schematic structure of a
transcription unit is given below:
(a)
Identify a, b and c.
(b)
The coding sequences/expressed
sequences in eukaryotes are known as ...................
16. (a) Expand ART.
(b) Suggest the ART which may be successful in the following
condition:
(i) Inability of the male partner to inseminate
the female.
(ii)
Female cannot produce ovum but can provide suitable environment for
fertilisation and further development.
III. Answer any 3 questions from 17
– 20. Each carries 3 scores. (3 x 3 = 9)
17. (a) The term ‘biodiversity’ was
popularised by .................
(b) Name the two types of biodiversity conservation.
(c) Write any three causes of biodiversity loss.
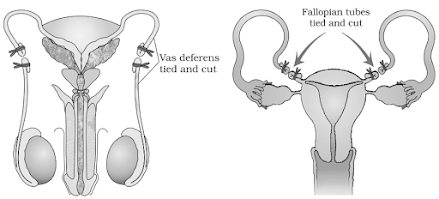
18. Observe the diagrams A and B given
below related to contraceptive methods.
(a)
Identify A and B.
(b)
Explain this surgical method.
(c)
Why this method is generally advised
as a terminal method of contraception?
19. Lactose catabolism in the absence of
inducer in E. Coli is given below:
(a)
Identify ‘P’.
(b)
Draw the diagram in the presence of
inducer.
(c)
Write the enzymes produced by the
structural genes ‘z’, ‘y’ and ‘a’.
20. Prepare a pamphlet as part of an
awareness programme in your school regarding the “Prevention and control of
Alcohol and Drug abuse in adolescents”.
[Hint: Prevention and control measures]